In recent years, the reliance on static SSH keys as a primary method for secure remote access has become a common practice across many organizations. The SSH (Secure Shell) protocol, which has been in use for over two decades, provides a way to securely connect to network resources. However, as companies grow and the number of servers and users increases, the limitations and vulnerabilities of static SSH keys become increasingly apparent.
Challenges with Static SSH Keys
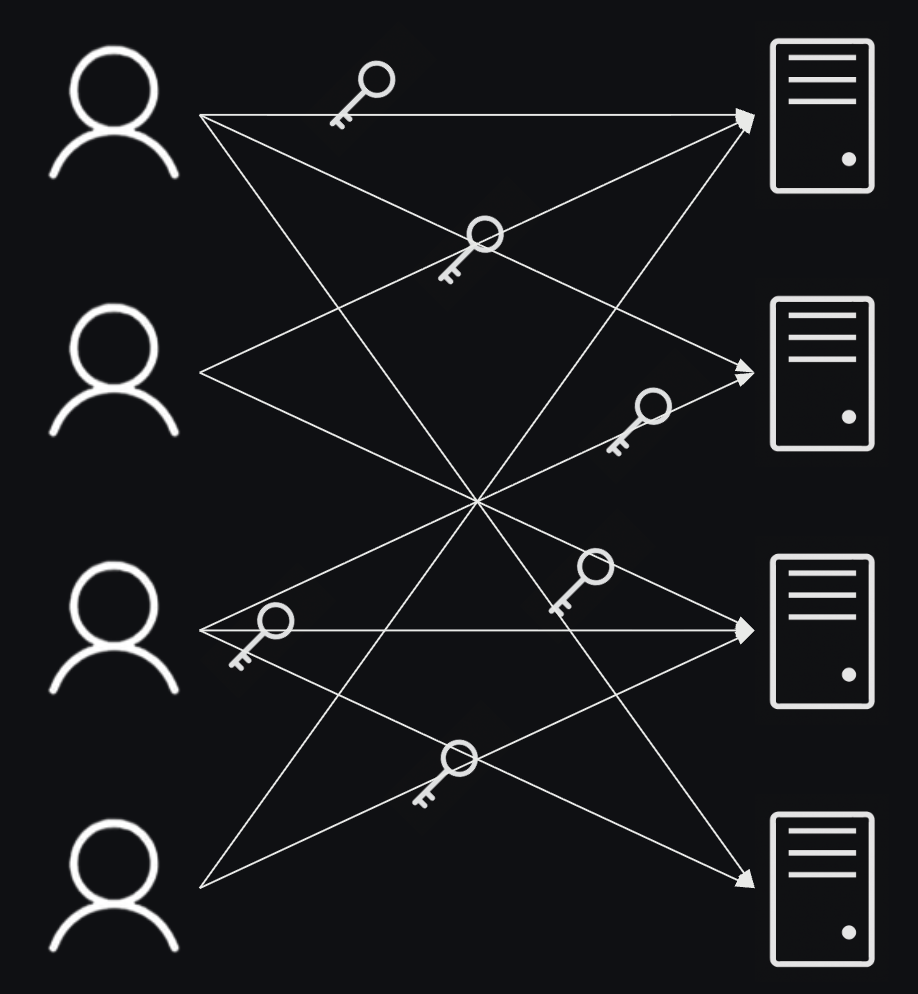
Static SSH keys consist of a public/private key pair. The public key is stored on the target server, while the private key is held by the user. This system works well for small environments but becomes cumbersome and insecure when scaled to larger operations. Here are some common issues associated with static SSH keys:
- Lack of Rotation: Static keys are often not rotated regularly, leading to potential security vulnerabilities. They can remain valid for long periods, increasing the risk of unauthorized access if a key is compromised.
- Key Sharing: Keys are frequently shared among multiple users or teams within an organization, which makes it difficult to track who accessed what and when.
- Operational Overhead: Managing a large number of keys across numerous devices can be resource-intensive and prone to human error.
- Third-Party Risks: Contractors and third-party vendors often require access, complicating key management and increasing the risk of breaches, especially if keys are not properly managed or rotated.
The inability to effectively audit and trace access with static keys is a significant concern. Without an audit trail, it’s challenging to determine who accessed a server or what actions were performed during a session. This lack of traceability can lead to security breaches going unnoticed.
Transitioning to SSH Certificates
A promising solution to these challenges is the use of SSH certificates. Unlike static keys, SSH certificates offer a scalable and secure alternative. They involve the use of a Certificate Authority (CA) to sign keys, thus providing several advantages:
- Scalability: SSH certificates can be centrally managed and easily scaled as organizations grow.
- Automatic Revocation and Expiration: Certificates have built-in expiration dates and can be revoked, reducing the risk associated with long-lived keys.
- Enhanced Security: By using certificates, organizations can ensure that access is granted only to authorized users, and the validity of the access can be controlled more effectively.
How SSH Certificates Work
The process involves generating a public/private key pair and having the public key signed by a CA. The CA can set criteria such as the validity period and the identity of the certificate holder. Once signed, the certificate can be used to authenticate to the target server. The server trusts the CA’s signature, allowing for secure access.
Benefits of SSH Certificates
- Centralized Management: Organizations can manage access through a centralized system, reducing the complexity and overhead of key management.
- Improved Security: With certificates, each access request can be individually verified and tracked, enhancing security and auditability.
- Reduced Risk: By limiting the lifespan of certificates and automating their rotation, the risk of unauthorized access is minimized.
Implementing SSH Certificates with Modern Solutions
To further streamline the management of SSH certificates, companies like HashiCorp offer solutions such as Vault and Boundary. These tools provide a robust framework for managing secrets and access in dynamic environments:
- HashiCorp Vault: Vault centralizes secrets management, allowing for the automatic rotation of credentials and reducing the reliance on static, long-lived keys. It offers an SSH secrets engine that facilitates secure authentication and authorization.
- HashiCorp Boundary: Boundary complements Vault by providing identity-driven controls for secure access. It integrates with Vault to dynamically generate and manage SSH certificates, offering passwordless connectivity through a process called credential injection.
Workflow with Vault and Boundary
- Key Generation: When a user initiates an SSH connection, a public/private key pair is generated.
- Certificate Signing: The public key is sent to Vault, where it is signed to create an SSH certificate.
- Credential Injection: Boundary injects the signed certificate into the session, allowing the user to authenticate without directly handling the credentials.
This approach enhances security by ensuring that credentials are short-lived and revoked after use, reducing the risk of exposure or misuse.
Additional Considerations
The transition from static SSH keys to certificates requires careful planning and implementation. Organizations must ensure they have the resources and expertise to manage the CA infrastructure and handle certificate requests effectively. However, the benefits in terms of security, auditability, and operational efficiency are significant.
Performance and Security of Encryption Algorithms
SSH certificates rely on existing encryption algorithms, such as RSA and ED25519. Each has its strengths:
- RSA: Known for its security, RSA uses larger key sizes, typically ranging from 2048 to 4096 bits.
- ED25519: Offers comparable security with smaller key sizes and faster performance, making it a popular choice for SSH certificates.
These algorithms ensure that the underlying cryptographic strength of SSH certificates remains robust, even as they provide enhanced flexibility and management capabilities.
Conclusion
The shift from static SSH keys to certificates represents a significant advancement in secure remote access management. By leveraging modern tools like HashiCorp Vault and Boundary, organizations can achieve a more secure, scalable, and manageable access framework. This transition not only addresses the inherent vulnerabilities of static keys but also aligns with best practices for credential management in today’s dynamic IT environments.
For organizations operating in multi-cloud or complex environments, adopting SSH certificates and integrating them with solutions like Vault and Boundary can offer a comprehensive, centralized approach to managing SSH access. This evolution not only enhances security but also simplifies compliance and reduces administrative burdens, paving the way for more efficient and secure operations.
For more Information, Refer to this article.