Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): A New Era in Nuclear Energy
In recent years, a significant shift has occurred in the global energy landscape, with countries looking for sustainable and reliable energy sources to meet their growing demands. Amidst this backdrop, Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) have emerged as a promising solution. Unlike traditional large nuclear reactors, SMRs are compact, cost-effective, and versatile, making them an attractive choice for many nations. China and Russia have already taken the lead by deploying their first SMR units, signaling a move towards a new era in nuclear energy.
At a time when the world is increasingly focusing on reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change, SMRs offer a pathway to cleaner energy. These reactors have lower initial investment costs and can be integrated seamlessly with renewable energy sources like solar and wind. This integration is crucial, especially after the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) held in Dubai, where a global consensus was reached to expand nuclear power as a viable alternative to fossil fuels.
Understanding the Role of SMRs
SMRs are designed to be much smaller than conventional nuclear reactors. This size reduction translates to several advantages: they require less capital investment, have shorter construction times, and offer greater flexibility in terms of deployment. Their smaller size also means they can be deployed in locations unsuitable for larger plants, bringing nuclear power to regions previously unable to benefit from this technology.
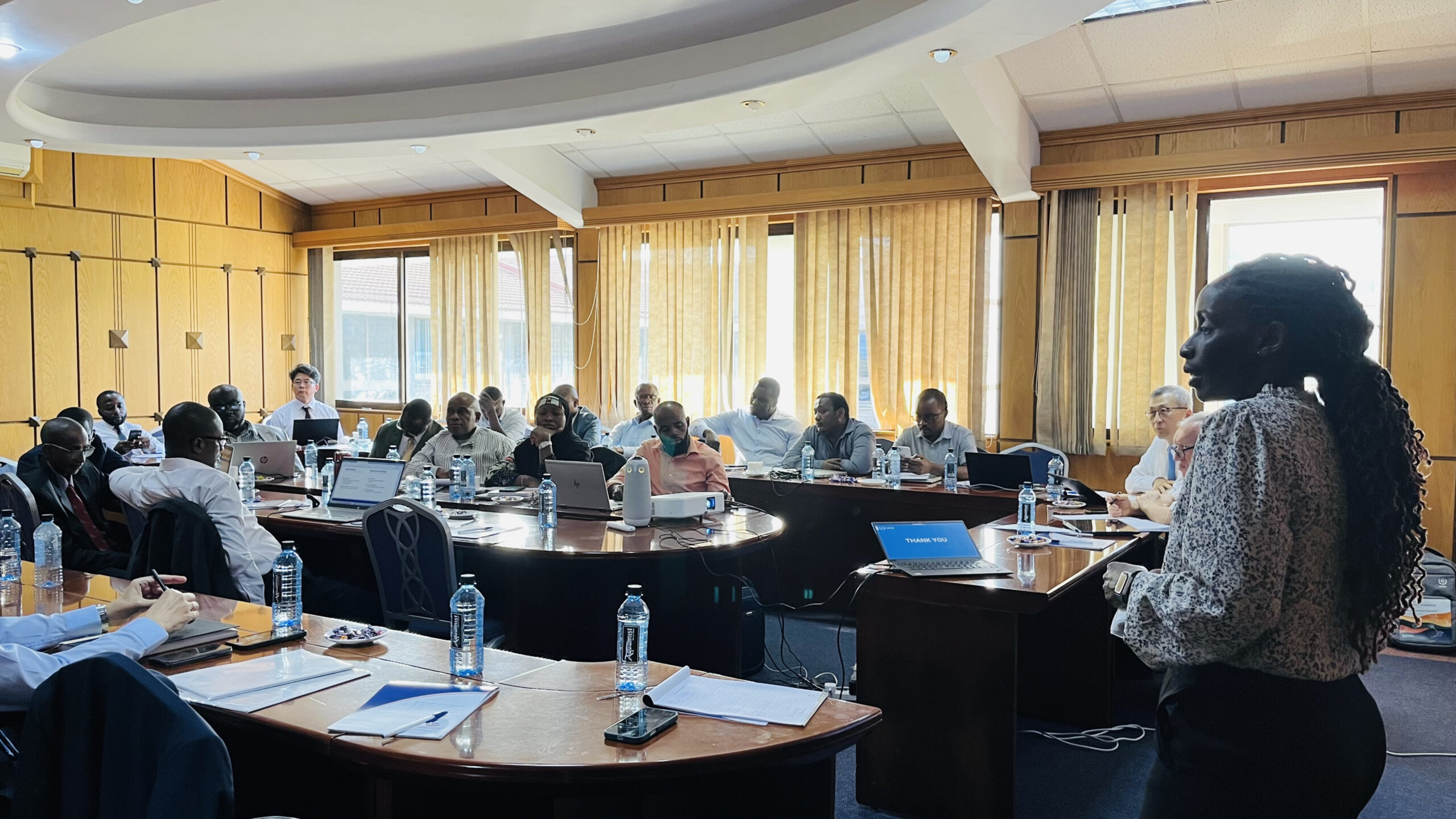
During the inaugural SMR School, an event designed for high-level officials, key aspects of SMRs were discussed. Topics included technological development and demonstration, the establishment of legal frameworks, stakeholder engagement, and the importance of safety, security, and safeguards. These discussions are essential as they provide a comprehensive understanding of what it takes to successfully develop and deploy SMRs.
Insights from Global Experts
Rasheed Adeola Ogunola from the Nigeria Atomic Energy Commission emphasized the value of the SMR School. He noted that the technical presentations, discussions, and shared experiences significantly enhanced the understanding of SMR deployment and regulatory considerations. This knowledge is crucial for countries like Nigeria as they progress through the milestones of nuclear power program development.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) plays a pivotal role in promoting the development and deployment of SMRs. Dohee Hahn, the IAEA Platform Coordinator, highlighted the importance of the new IAEA SMR School. According to Hahn, this initiative aims to bridge the knowledge gap and help countries understand the complexities involved in adopting SMR technology. As nations strive to find clean and reliable solutions to their energy challenges, nuclear energy, particularly through SMRs, is becoming an increasingly attractive option.
The Advantages of SMRs
- Cost Efficiency: One of the primary benefits of SMRs is their lower upfront costs. Smaller reactors require less investment compared to their larger counterparts, making them financially accessible to more countries.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SMRs can be scaled according to demand. This scalability means that countries can start small and gradually increase their nuclear capacity as needed. Furthermore, their ability to work alongside renewable energy sources allows for a more balanced and resilient energy grid.
- Safety Enhancements: Modern SMR designs incorporate advanced safety features. These reactors are engineered to shut down safely in the event of an emergency, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Reduced Construction Time: The smaller size of SMRs allows for faster construction, which means that they can be brought online more quickly to meet immediate energy needs.
- Environmental Benefits: By replacing fossil fuel-based power sources, SMRs contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and transition to cleaner energy sources.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, the deployment of SMRs is not without challenges. Countries must navigate complex regulatory environments, ensure adequate safety and security measures, and engage stakeholders effectively. Robust legal frameworks need to be established to support the safe operation of these reactors. Moreover, public perception and acceptance are crucial, as communities must understand and trust the safety and benefits of nuclear energy.
Looking Forward
The future of SMRs looks promising as more countries invest in this technology. The global push for cleaner energy sources is likely to accelerate the adoption of SMRs, with more nations following the lead of China and Russia. The IAEA’s initiatives, such as the SMR School, are instrumental in equipping countries with the knowledge and tools necessary to embark on their nuclear journeys.
Conclusion
Small Modular Reactors represent a transformative approach to nuclear energy. Their compact size, cost-effectiveness, and ability to integrate with renewable sources make them a key player in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. As the world grapples with the dual challenges of increasing energy demand and reducing carbon emissions, SMRs offer a viable path forward. By addressing regulatory, safety, and public perception issues, countries can harness the full potential of this innovative technology and pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future.
For more information on the global developments in nuclear energy and the role of SMRs, readers can refer to detailed reports and publications from the International Atomic Energy Agency and other reputable sources.
For more Information, Refer to this article.