NASA’s Innovative Athena EPIC Mission: A New Era in Space Technology
NASA is embarking on an exciting venture with the Athena Economical Payload Integration Cost mission, commonly referred to as Athena EPIC. This mission represents a significant leap forward in space technology, aiming to revolutionize how space missions are conducted. Athena EPIC is a test launch designed to evaluate a groundbreaking, scalable space vehicle design that promises to support future missions more efficiently. By sharing resources among the payloads onboard and managing routine functions, this small satellite platform reduces the need for individual payloads to handle these tasks independently.
Cost-Effective and Efficient Space Exploration
The primary advantage of the Athena EPIC mission is its potential to significantly lower costs and accelerate the timeline for launching into space. This is achieved by consolidating resources, which not only reduces taxpayer burden but also streamlines the process of getting missions off the ground. According to Clayton Turner, Associate Administrator for Space Technology Mission Directorate at NASA headquarters in Washington, "Increasing the speed of discovery is foundational to NASA. Our ability to leverage access to innovative space technologies across federal agencies through industry partners is the future." Turner emphasizes that Athena EPIC exemplifies the government operating at its best—advancing knowledge with existing hardware integrated with new technologies.
Collaboration with Key Partners
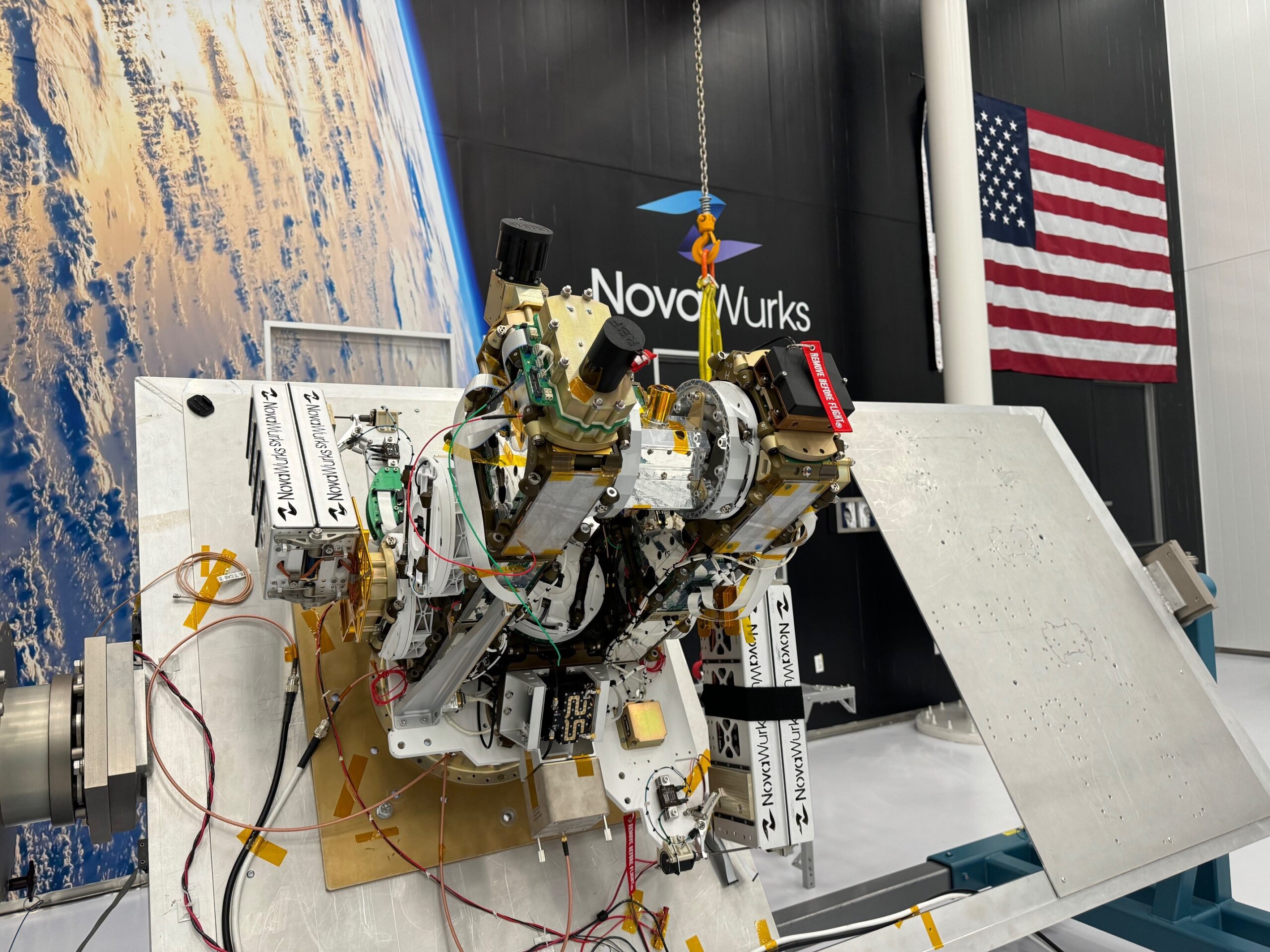
The Athena EPIC mission is a collaborative effort involving multiple government and industry partners. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the U.S. Space Force are among the government partners contributing to this demonstration mission. Additionally, NovaWurks, a leading industry partner, has provided the space vehicle platform. This platform is built using a novel technology called Hyper-Integrated Satlet, or HISat.
Understanding HISat Technology
HISat technology can be likened to a child’s toy made of interlocking building blocks. These components are designed to be assembled into larger structures known as SensorCraft. The SensorCraft can share resources among numerous payloads and adapt to different sizes and shapes to accommodate various missions. This modular, building-block architecture offers significant flexibility in payload design, ultimately providing payload providers with easier and more affordable access to space. Moreover, it allows for increased maneuverability between multiple orbits.
A Closer Look at the Athena Sensor Payload
The Athena sensor payload was meticulously designed and constructed by scientists at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. It comprises an optical module, a calibration module, and a newly developed sensor electronics assembly. Interestingly, the sensor for Athena EPIC was built using spare parts from NASA’s Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) mission, which has been instrumental in tracking Earth’s radiation budget over several generations of satellite and space station instruments.
Integration and Simplification with SensorCraft
Kory Priestley, the principal investigator for Athena EPIC from NASA Langley, highlights a crucial aspect of this mission: instead of requiring its own processor, Athena relies on the processors within the HISats to control essential functions such as heaters. This approach merges an instrument with a satellite platform, forming what is termed a SensorCraft. Such integration means that the primary instrument does not need as many built-in capabilities, as these are provided by the satellite host. This design not only offers greater redundancy but also simplifies the payload, making it more efficient.
The First of Its Kind
Athena EPIC is the inaugural HISat mission led by NASA. Traditional satellites, like those hosting CERES instruments, are often large and custom-built, requiring extensive hardware and software for various control and operational functions. These satellites can be as large as a school bus and may even include redundant systems to mitigate potential failures. This complexity, coupled with the need for larger launch vehicles, significantly drives up costs.
Transforming Earth Observation
The innovative approach embodied by Athena EPIC promises to drastically cut costs, reducing expenses from billions to millions per mission. Priestley notes, "Now we are talking about something much smaller—SensorCraft the size of a mini refrigerator." This compact design means that in the event of a failure in orbit, replacements can be made much more economically. This marks a significant shift in the methodology for Earth observation and space exploration.
Upcoming Launch and Future Prospects
Athena EPIC is scheduled for a launch on July 22, sharing a ride on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket departing from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The primary NASA payload on this launch will be the Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites (TRACERS) mission. Led by the University of Iowa for NASA’s Heliophysics Division within the Science Mission Directorate, the TRACERS mission underscores the collaborative nature of modern space exploration. NASA’s Earth Science Division has also contributed funding for Athena EPIC.
A New Path for Satellite Development
Langley Research Center has long been a pioneer in developing remote sensing instruments for in-orbit satellites. As satellites continue to shrink in size, a more unconventional and efficient path to launch becomes essential. This approach aims to reduce complexity while simultaneously enhancing the value of exploration, science, and technology measurements for the nation. As Turner points out, these advancements will enable a new era of satellite development characterized by smaller, more versatile platforms that maintain high scientific value.
Conclusion: A Promising Step Forward
In summary, the Athena EPIC mission represents a promising step forward in space technology, offering a more cost-effective and efficient means of conducting space missions. By integrating innovative technologies and fostering collaboration among government agencies and industry partners, NASA is paving the way for the future of space exploration. The success of this mission could serve as a blueprint for future endeavors, enabling faster discoveries and expanding our understanding of the universe. For more detailed information about the Athena mission, interested readers can visit NASA’s official website.
In conclusion, the Athena EPIC mission exemplifies the potential of innovative technologies to transform space exploration, making it more accessible and cost-effective. By leveraging existing hardware and integrating new technologies, NASA is setting the stage for a future where space missions are not only more efficient but also more impactful. As this mission progresses, it will be interesting to see how these advancements influence future space endeavors and contribute to a deeper understanding of our universe.
For more Information, Refer to this article.