NASA’s X-59 Quiet Supersonic Aircraft Makes Significant Progress with Initial Taxi Test
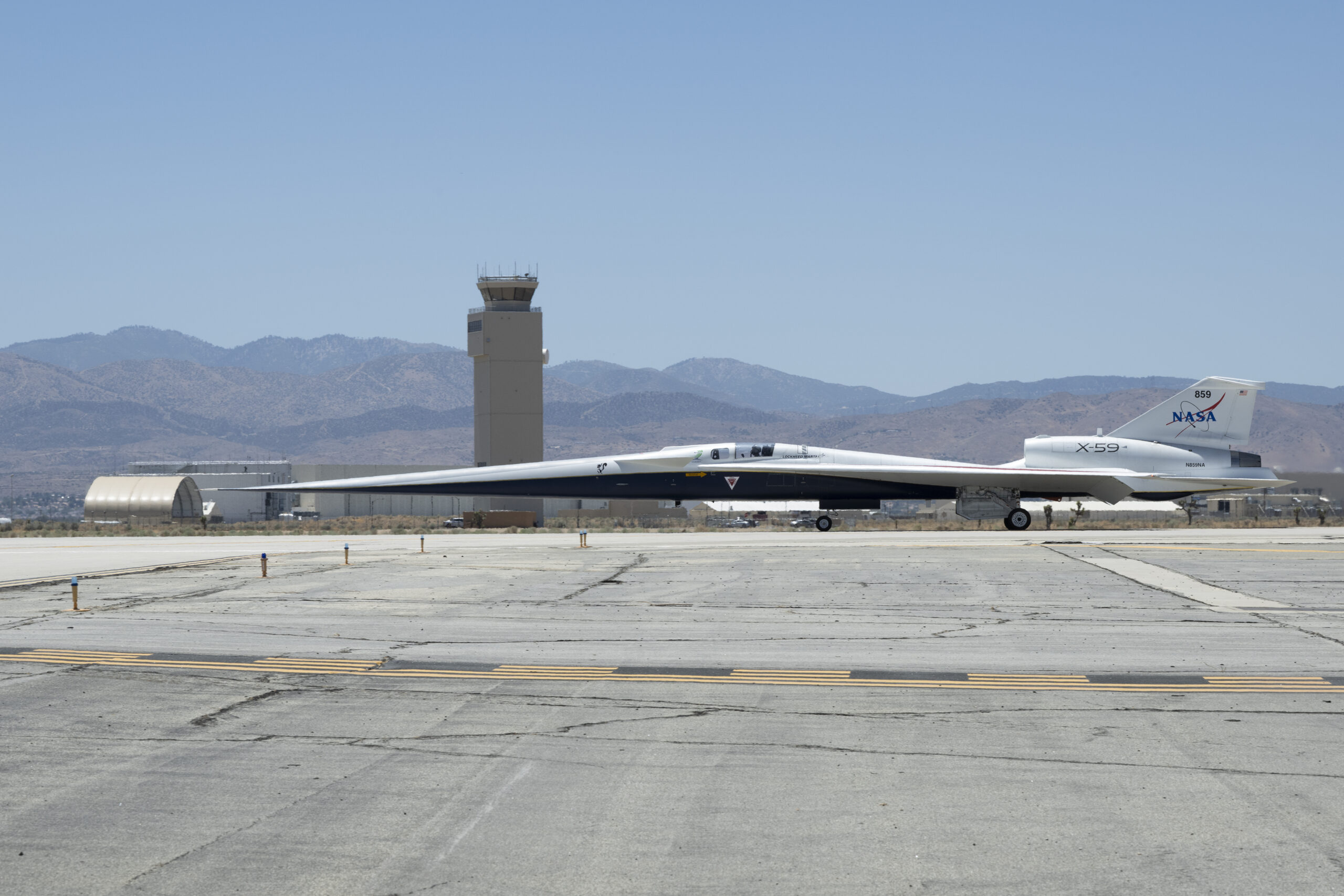
In a remarkable advancement for aerospace technology, NASA’s X-59, an innovative supersonic research aircraft, has successfully completed its first low-speed taxi test at the U.S. Air Force Plant 42 located in Palmdale, California. This event, dated July 10, 2025, marks a pivotal moment for NASA, as it is the first occasion the uniquely designed aircraft has maneuvered using its own propulsion system.
During this crucial test, engineers and flight crews closely observed the X-59 as it traversed the runway. The primary goal was to ensure the proper functionality of its essential systems, including steering and braking mechanisms. Successfully completing these taxi tests signifies the commencement of the X-59’s concluding series of ground tests before it is cleared for its inaugural flight.
X-59: The Flagship of NASA’s Quesst Mission
The X-59 is an integral component of NASA’s ambitious Quesst mission. The mission’s primary objective is to showcase the feasibility of quiet supersonic travel by significantly diminishing the disruptive sonic boom to a more subdued "thump." Traditional supersonic flights generate a loud sonic boom when they break the sound barrier, which not only disrupts communities but also restricts overland supersonic travel. By addressing this issue, NASA hopes to pave the way for a new era of commercial supersonic air travel that is both efficient and community-friendly.
The Science Behind Quiet Supersonic Flight
To understand the significance of the X-59, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of supersonic flight and the challenges it presents. When an aircraft travels faster than the speed of sound, it creates shock waves that merge to produce a sonic boom. This abrupt change in pressure is not just a loud noise; it can also cause minor structural damage and disturb wildlife.
The X-59 is engineered to minimize this effect through its unique design. Its elongated fuselage and carefully crafted aerodynamics help in reshaping the shock waves, thus lessening the intensity of the sonic boom. Instead of the typical boom, the aircraft is expected to produce a softer thump, which is less likely to disturb people on the ground.
The Road Ahead: Ground Tests to First Flight
The recent low-speed taxi test is just the beginning of a series of evaluations that the X-59 must undergo. These ground tests are designed to rigorously assess every aspect of the aircraft’s performance and safety. Following the low-speed tests, the X-59 will proceed to high-speed taxi tests. These will further challenge the aircraft, pushing its systems to their limits to ensure they can withstand the rigors of supersonic flight.
Once the ground tests are successfully concluded, the X-59 will be ready for its first flight. This milestone will not only mark a significant achievement for NASA but also a giant leap forward in the field of aeronautics.
Implications for Future Air Travel
The successful development and deployment of the X-59 have far-reaching implications for the future of air travel. If NASA’s Quesst mission achieves its goals, it could revolutionize the aviation industry by making supersonic travel over land a reality. This would drastically reduce flight times across continents, offering a faster alternative for long-distance travel.
Moreover, the technology developed for the X-59 could be adapted for commercial airliners, potentially leading to quieter and more efficient aircraft in the future. This would not only benefit passengers but also reduce the environmental impact of air travel, aligning with global efforts to create more sustainable transportation solutions.
Industry Reactions and Future Prospects
The aerospace industry is watching NASA’s progress with the X-59 closely. Many experts believe that the successful implementation of quiet supersonic technology could trigger a new wave of innovation in aircraft design and operation. Companies involved in the development of next-generation aircraft are likely to leverage the findings from the Quesst mission to enhance their own projects.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies worldwide are keenly interested in the outcomes of the X-59’s tests. The ability to mitigate sonic booms could lead to revised regulations, allowing for the expansion of supersonic flight paths over populated areas, which are currently restricted.
Conclusion
NASA’s X-59 project represents a groundbreaking effort to reshape the future of supersonic flight. By tackling the challenge of sonic booms, NASA is not only working to make the skies quieter but also opening the door to faster, more efficient air travel. As the X-59 continues its journey from ground tests to its first flight, the world will be watching closely, eager to see how this pioneering aircraft will influence the future of aviation.
For more Information, Refer to this article.